Management insight KPIs drive execution success. Quantifiable performance indicators drive strategic and tactical modifications to existing activities to optimize market performance.
Two primary KPI categories achieve this objective:
- Performance KPIs measure degrees of success and failure for specific goal achievement and processes. An example of a performance‑based KPI is digital sales conversion that shows ratios of attraction to interest to executed action. Performance over time indicates effectiveness of website content and early customer engagement through fulfillment processes.
- Predictive KPIs quantify probability. Predictive KPIs indicate likely customer attrition and sales performance forecasts based on pipeline content. Effective management insight KPIs include drill-down capability, making the appropriate level of detail available to identify root causes. This makes KPIs actionable. With this capability, institutions can identify constraints, issues, and opportunities for improvement so that best practices can be incorporated into execution strategy.
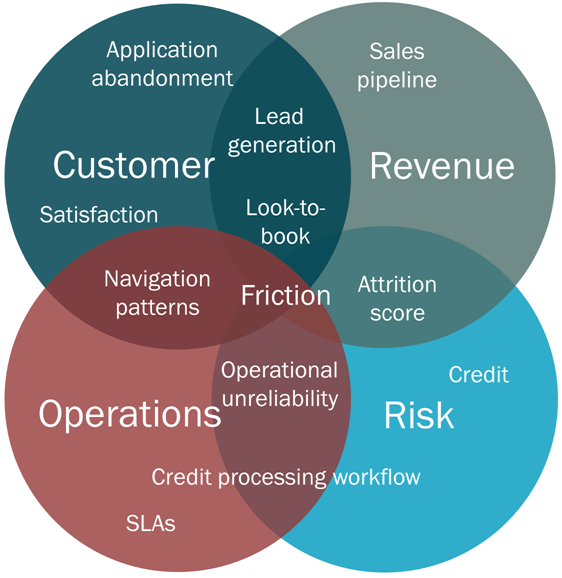
Management insight KPIs span the following Connects functional areas:
- Customer—Insight through the customer journey starting from first website touch through relationship expansion
- Revenue—Acquisition, pipeline management, and sales forecasting
- Operations—Fulfillment, service requests, and reliability
- Risk—Customer identification and suspicious activity, operational risk, and credit risk exposure
For more information, download the “Optimizing Performance Through Management Insight” interview with David Engebos, President and COO of ARGO.